
A test for depression should be able to detect depression in different age groups, for people in different socio-economic statuses, or introverts. For example, a claim that individual tutoring improves test scores should apply to more than one subject (e.g. External reliability means that your test or measure can be generalized beyond what you’re using it for. Internal reliability, or internal consistency, is a measure of how well your test is actually measuring what you want it to measure.

Cronbach’s alpha: measures internal reliability for tests with multiple possible answers.Kuder-Richardson 20: a measure of internal reliability for a binary test (i.e.There are many statistical tools you can use to measure reliability. Of course, it’s not quite as simple as saying you think a test is reliable. In the same way, a reliable math test will accurately measure mathematical knowledge for every student who takes it and reliable research findings can be replicated over and over. For example, a medical thermometer is a reliable tool that would measure the correct temperature each time it is used. You can also think of it as the ability for a test or research findings to be repeatable. Reliability is a measure of the stability or consistency of test scores.
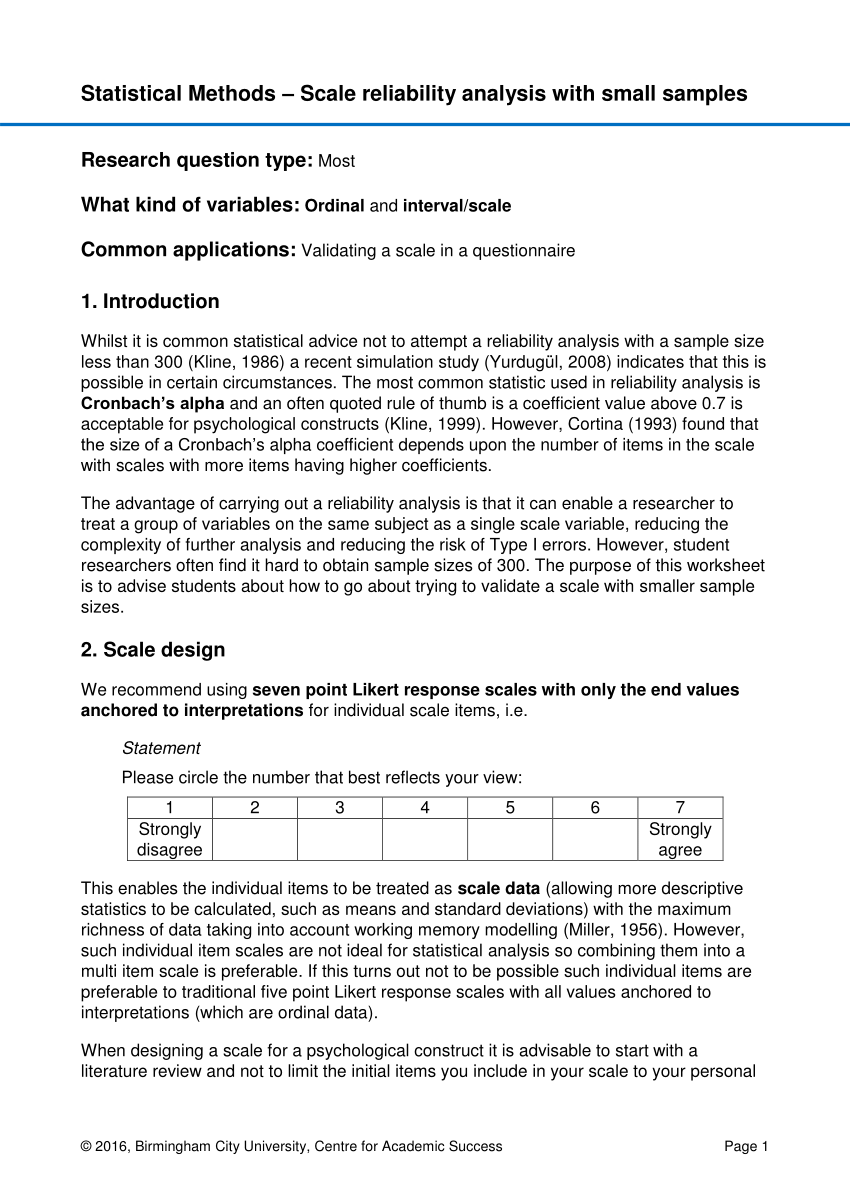
It would be reliable (giving you the same results each time) but not valid (because the thermometer wasn’t recording the correct temperature). For example, let’s say your thermometer was a degree off. However, tests that are reliable aren’t always valid. The ACT is valid (and reliable) because it measures what a student learned in high school. A test is valid if it measures what it’s supposed to. Reliability implies consistency: if you take the ACT five times, you should get roughly the same results every time. For research and testing, there are subtle differences.

Outside of statistical research, reliability and validity are used interchangeably.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
